Varicocele (Infertility)
Create a requestA varicocele surgery, also known as varicocelectomy, is a procedure aimed at improving male fertility and relieving pain associated with varicoceles. Varicoceles are enlarged veins in the scrotum that can cause decreased sperm production and quality, potentially leading to infertility.
General
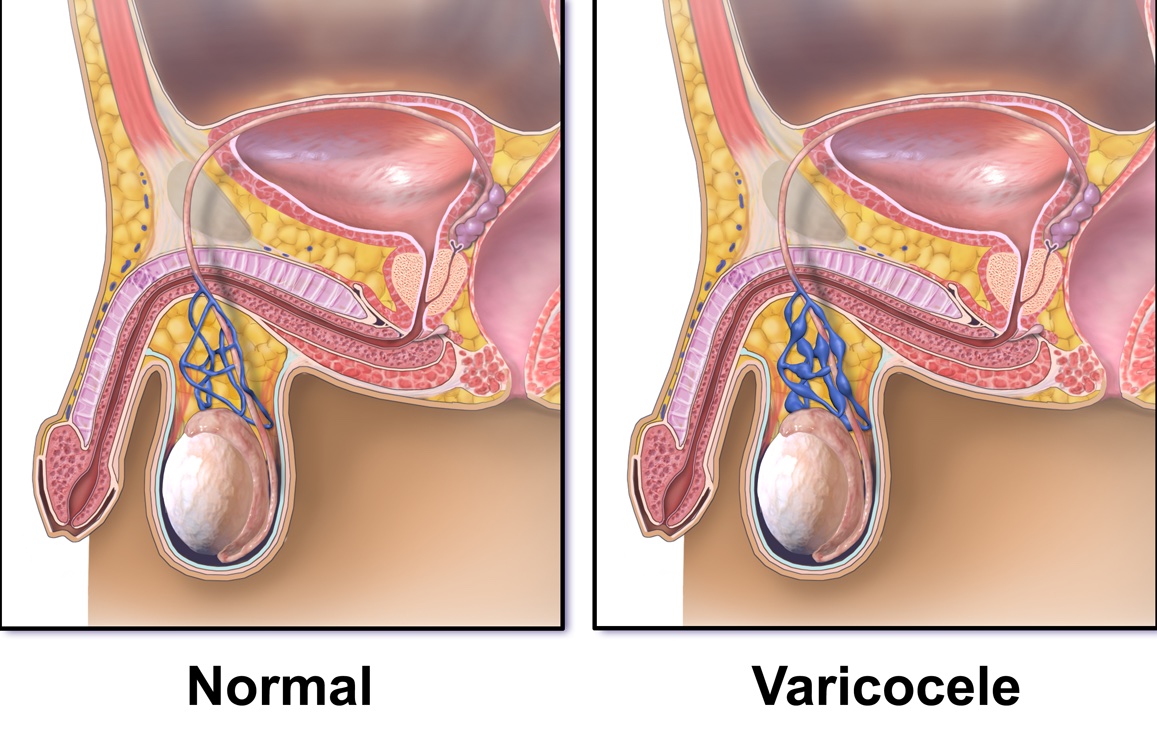
Varicocele surgery involves the identification and interruption of the abnormal veins that allow blood to pool, thus improving blood flow and potentially enhancing sperm production and quality. There are various surgical methods, including open surgery (through an incision in the groin), laparoscopic surgery (using small incisions and a camera to guide the procedure), and microsurgical techniques (using a surgical microscope for precision). This procedure is typically performed on an outpatient basis, meaning the patient can return home the same day. Post-surgery, the improved blood flow can lead to a significant improvement in the patient's fertility and a reduction in discomfort if it was present. Overall, the aim of varicocele surgery is not only to alleviate the symptoms associated with varicoceles, such as pain and testicular atrophy, but also to enhance the affected individual's fertility. By effectively disrupting the reflux of blood within the varicocele, the procedure aims to normalize scrotal temperature, which is thought to improve sperm production and function. Recovery times vary, but most men can return to normal activities within a week, with heavy lifting and strenuous activities advised against for a longer period.
Special Details
Who is it for?
Men experiencing infertility with a clinical diagnosis of varicocele.
Individuals with varicocele-associated testicular pain.
Men with a varicocele and abnormal semen parameters.
Recovery Period
Procedure duration: Generally takes around 1 to 2 hours.
Recovery duration: Most are able to return to work within a few days to a week, but full recovery can take up to 4-6 weeks.
Physical activity should be limited for the first 2 weeks post-surgery.
Potential Risks and Side Effects
Infection at the incision site.
Hydrocele formation (accumulation of fluid around the testicle).
Recurrence of varicocele.
Damage to the testicular artery leading to testicular atrophy.
Alternative Treatments
Embolization: A less invasive procedure where a coil is used to block blood flow to the varicocele.
Conservative treatment: Pain and symptoms can be managed with anti-inflammatory medications, supportive underwear, and lifestyle modifications.
Success Rate
Success rates for improving semen quality and fertility outcomes range from 60 to 80%, depending on the surgical technique and underlying patient factors.
Procedure step-by-step overivew
Pre-operative evaluation and imaging to locate the varicocele.
Anesthesia is administered to ensure the patient feels no pain during the procedure.
A small incision (in open surgery) or multiple small incisions (in laparoscopic or microsurgical methods) is made near the scrotum or groin.
Identification and isolation of the malfunctioning veins.
Ligation (tying off) of the veins with sutures, or removal of the veins.
Closure of the incision(s) with sutures or staples.
Post-operative care instructions are provided before the patient is sent home.
Prices
Turkey
$1,500 - $4,000
Czech Republic
$2,000 - $5,000
Croatia
$2,000 - $4,500
Lithuania
$1,800 - $4,000
Poland
$1,700 - $4,500
Germany
$5,500 - $7,500
Switzerland
$7,000 - $10,000
France
$3,500 - $7,000
United Kingdom
$3,000 - $6,500
United States
$4,000 - $15,000
Canada
$3,000 - $6,000
Australia
$4,500 - $9,000
Why Do Prices Vary?
Choice of surgical technique (open, laparoscopic, microsurgical).
Hospital or surgical center where the procedure is performed.
Geographical location.
Surgeon's experience and expertise.
Need for anesthesia and the type used.
Post-operative care and follow-up visits.