Diagnosis and Treatment of Lung Cancer
Create a requestThe diagnosis and treatment of lung cancer involves a multi-faceted approach aimed at detecting and managing one of the most common and serious types of cancer. It typically starts with imaging and biopsy to confirm the presence of cancer, followed by a tailored treatment plan that may include surgery, radiation, chemotherapy, targeted therapy, or a combination of these treatments.
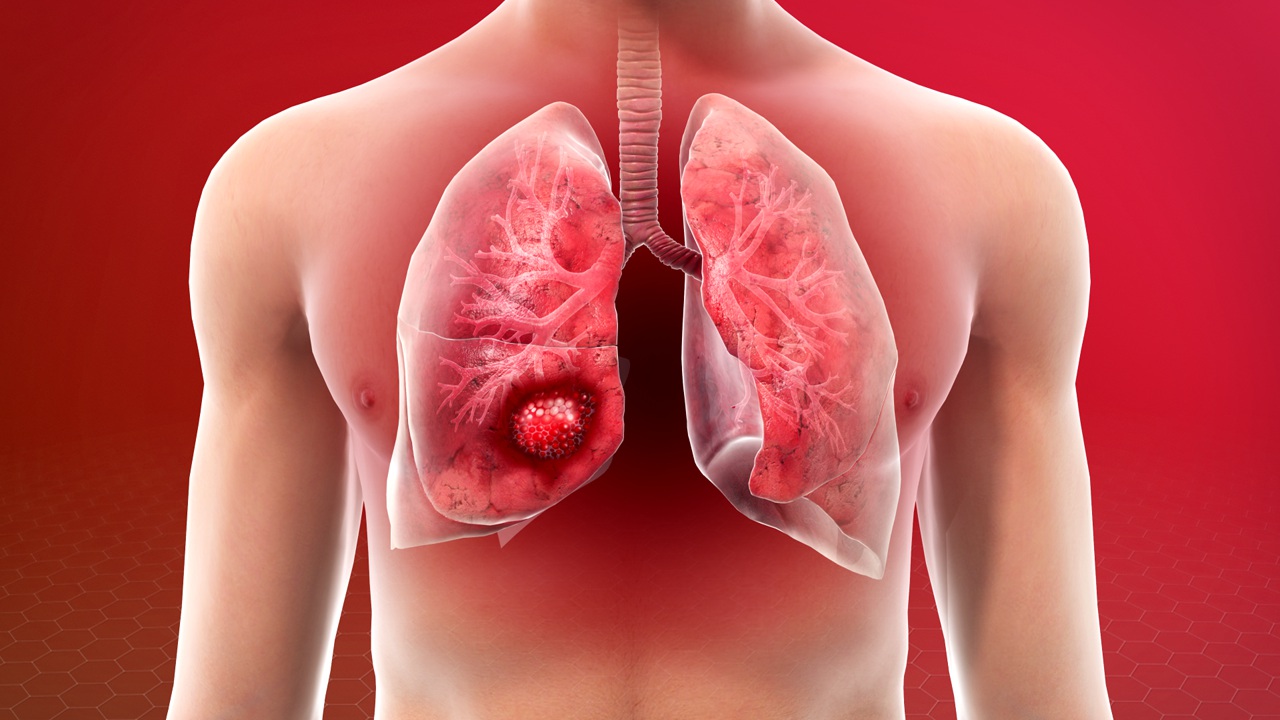
General
The journey to diagnosing lung cancer often begins with imaging tests such as chest X-rays and CT scans to identify abnormal masses or nodules in the lungs. If these tests suggest the possibility of cancer, further examination through a biopsy, where a small sample of lung tissue is collected and examined under a microscope, is typically conducted. The type, extent, and stage of lung cancer are determined through these diagnostic tests, which then guide the creation of a customized treatment plan. Treatment options vary widely depending on the cancer's stage and type, the patient's overall health, and preferences. Early-stage lung cancer might be addressed with surgical procedures to remove the tumor, while more advanced cancers could necessitate a combination of chemotherapy, radiation therapy, and targeted drug therapies. Recent advancements in medical science have also introduced immunotherapy as a promising treatment option for certain types of lung cancer, aiming to boost the body’s immune system to fight the cancer cells more effectively.
Special Details
Who is it for?
Individuals showing symptoms of lung cancer such as a persistent cough, coughing up blood, chest pain, and difficulty breathing.
Patients diagnosed with early-stage lung cancer, for whom surgical resection might offer a potential cure.
Patients with advanced lung cancer, including those who might benefit from chemotherapy, radiation therapy, targeted therapy, or immunotherapy.
High-risk individuals, including heavy smokers or those with a significant history of smoking, who may undergo screening for lung cancer.
Recovery Period
The procedure time varies widely: surgery might last 2-4 hours, chemotherapy cycles typically span several weeks, and radiation therapy can range from daily treatments over several weeks to a few high-dose sessions.
Recovery time is highly individual and depends on the specific treatment, ranging from weeks for surgical recovery to months for the full effects of chemotherapy or radiation therapy to manifest.
Potential Risks and Side Effects
Surgery risks include bleeding, infection, and complications from anesthesia.
Chemotherapy and radiation therapy may cause nausea, vomiting, fatigue, hair loss, and increased susceptibility to infections.
Targeted therapy and immunotherapy risks include skin reactions, high blood pressure, and potential effects on normal organ function.
Alternative Treatments
Palliative care to manage symptoms and improve quality of life.
Participation in clinical trials to access new and potentially effective treatments not yet available widely.
Radiosurgery for certain small, localized tumors.
Success Rate
["The success rate varies significantly based on the cancer's stage at diagnosis. Early-stage lung cancer has a 5-year survival rate of about 60% when treated surgically, but advanced lung cancer has a significantly lower survival rate.", 'Recent treatment advancements have improved outcomes for certain types of advanced lung cancer.']
Procedure step-by-step overivew
Initial diagnosis through imaging tests such as X-rays and CT scans.
If abnormalities are detected, a biopsy is performed to confirm the presence of cancer cells.
Staging of the cancer through additional imaging tests to determine the extent and spread.
Development of a tailored treatment plan based on the cancer's stage, type, and the patient's health.
Surgical removal of the tumor, if applicable, followed by chemotherapy and/or radiation therapy as needed.
Follow-up care and monitoring for recurrence or side effects of treatment.
Prices
Turkey
USD 15,000 - 25,000
Czech Republic
USD 20,000 - 30,000
Croatia
USD 20,000 - 28,000
Lithuania
USD 18,000 - 25,000
Poland
USD 15,000 - 22,000
Germany
USD 30,000 - 45,000
Switzerland
USD 35,000 - 50,000
France
USD 28,000 - 40,000
United Kingdom
USD 25,000 - 40,000
United States
USD 70,000 - 100,000
Canada
USD 20,000 - 30,000
Australia
USD 25,000 - 35,000
Why Do Prices Vary?
The type and stage of lung cancer being treated.
The specific combination of treatments used, including surgery, chemotherapy, radiation therapy, targeted therapy, or immunotherapy.
Geographical location and the facility where treatment is provided.
Insurance coverage and out-of-pocket expenses for the patient.