Diagnosis And Treatment Of Cervical Cancer
Create a requestThe diagnosis and treatment of cervical cancer involves a series of procedures aimed at identifying the presence of cancer cells in the cervix and implementing strategies to treat or manage the condition. These procedures range from initial screening tests, like Pap smears, to more advanced diagnostic tools, and treatment methods including surgery, radiation therapy, and chemotherapy.
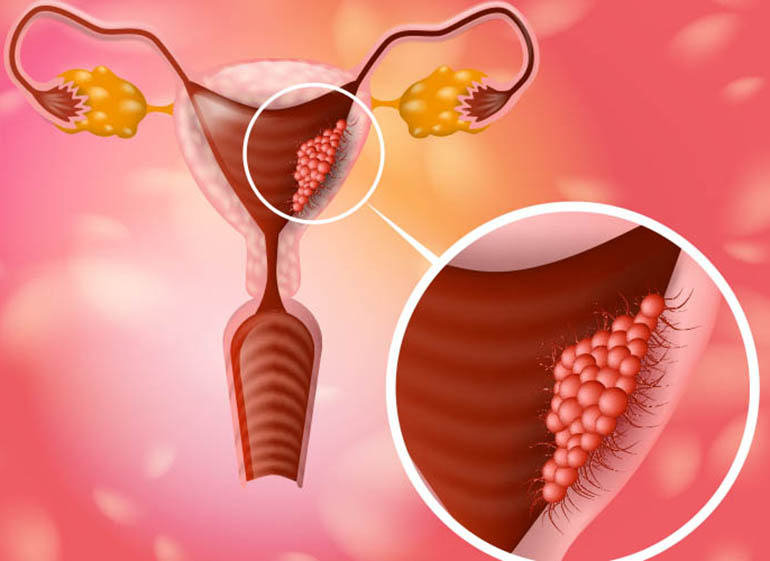
General
Cervical cancer diagnosis begins with routine screenings, the most common being the Pap test, which can detect precancerous or cancerous cells on the cervix. If abnormal cells are found, further diagnostic tests such as HPV testing, colposcopy, or a biopsy may be recommended to determine the presence and extent of cervical cancer. Following a confirmed diagnosis, the treatment plan is tailored to the individual's stage of cancer, overall health, and treatment preferences. Options typically include surgery (to remove cancerous tissue), radiation therapy (to destroy cancer cells), chemotherapy (to stop the growth of cancer cells), or a combination of these treatments. The goal of treatment is to eliminate cancer, prevent its spread, and minimize side effects and complications.
Special Details
Who is it for?
Women with a confirmed diagnosis of precancerous lesions or cervical cancer.
Individuals at high risk of cervical cancer due to HPV infection, smoking, having a weakened immune system, long-term use of birth control pills, or a history of cervical cancer in the family.
Women who have abnormal results from routine cervical cancer screenings.
Recovery Period
The time required for the procedure and recovery varies significantly depending on the treatment method. Surgical treatments may require hospital stays of a few days with several weeks to recover, while chemotherapy and radiation therapy could extend over several months.
Full recovery and return to normal activities can vary from a few weeks for minor surgical procedures to several months for more extensive treatments.
Potential Risks and Side Effects
Surgical risks include infection, bleeding, and damage to nearby organs.
Radiation therapy may cause side effects like fatigue, skin irritation, and changes in bowel or bladder habits.
Chemotherapy can have side effects such as nausea, hair loss, and an increased risk of infection.
Long-term risks may include sexual dysfunction and potential fertility issues.
Alternative Treatments
Preventive HPV vaccination to reduce the risk of developing cervical cancer.
Regular screening and monitoring of precancerous conditions without immediate treatment, known as 'watchful waiting'.
Use of targeted therapy drugs that focus on specific abnormalities in cancer cells.
Immunotherapy to boost the body's natural defenses to fight the cancer.
Success Rate
The success rate of treating cervical cancer significantly depends on the stage at which the cancer is diagnosed and treated. Early-stage cervical cancer has a high treatment success rate of over 90%, while advanced cancer stages have lower survival rates.
Procedure step-by-step overivew
Initial screening and detection through Pap smears or HPV testing.
Follow-up diagnostic tests such as colposcopy or biopsy if initial tests are abnormal.
Assessment of cancer stage through imaging tests like MRI, CT scans, or PET scans.
Developing a personalized treatment plan considering the stage of cancer, patient's health, and preference.
Implementation of the treatment plan, which may include surgery, radiation therapy, chemotherapy, or a combination.
Post-treatment follow-up to monitor for signs of recurrence and manage any side effects or complications.
Prices
Turkey
$3,000 - $10,000
Czech Republic
$4,500 - $12,000
Croatia
$4,000 - $11,000
Lithuania
$5,000 - $13,000
Poland
$4,500 - $12,000
Germany
$8,000 - $20,000
Switzerland
$12,000 - $30,000
France
$9,000 - $25,000
United Kingdom
$8,000 - $22,000
United States
$15,000 - $100,000
Canada
$8,000 - $25,000
Australia
$10,000 - $28,000
Why Do Prices Vary?
Type of treatment required (surgery, radiation, chemotherapy, combination therapies).
Geographical location of the treatment center.
Duration and complexity of the treatment.
Hospital stays, if necessary, and associated medical services.
Insurance coverage and reimbursement policies.